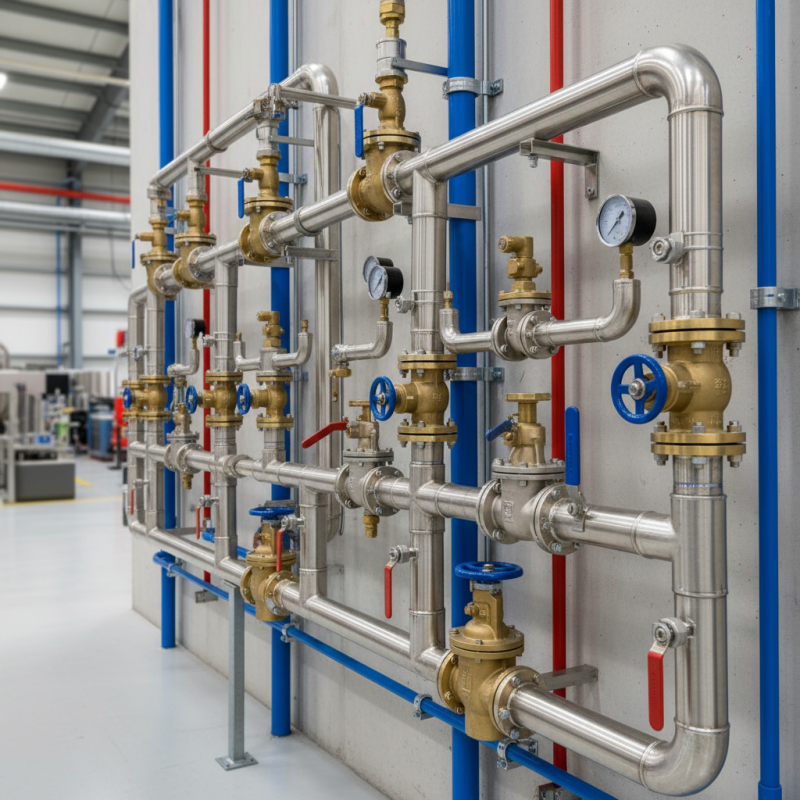
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial piping systems, the role of fittings and valves cannot be overstated. These components are crucial in ensuring efficient fluid management, influencing not only the operational reliability but also the overall energy consumption of the system. According to a report by the Global Piping Systems Market Analysis, the integration of high-quality fittings and valves can lead to up to a 30% reduction in energy costs, thereby enhancing sustainability efforts within the industry. As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency and cost-effectiveness, the selection of appropriate fittings and valves emerges as a critical component of design and maintenance strategies.
The effectiveness of a piping system is fundamentally dependent on the intricacy of its fittings and valves. A well-structured network of these components can significantly minimize flow restrictions and reduce the likelihood of leaks, which are often cited as major sources of operational failures. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) emphasizes that improper fitting choices can lead to increased maintenance needs and downtime, costing businesses millions annually. Thus, understanding the top fittings and valves available on the market and how they contribute to the efficiency of piping systems is essential for engineers and decision-makers striving to optimize their operations.

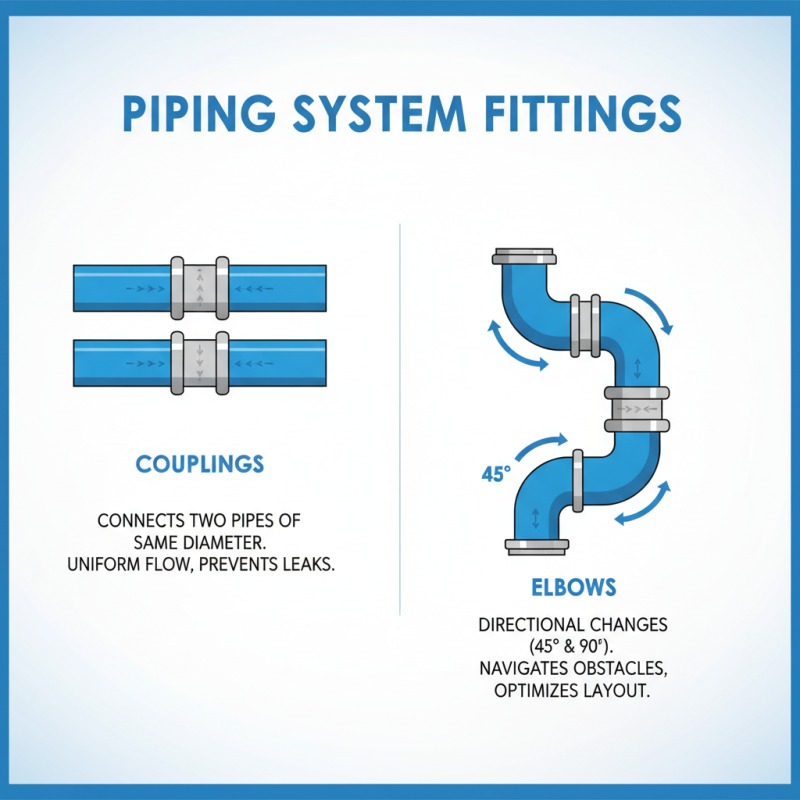
When designing piping systems, selecting the right fittings is crucial for ensuring seamless connections and efficient flow. Among the essential types of fittings are couplings, which connect two pipes of the same diameter, allowing for a smooth transition. They are particularly useful in maintaining a uniform flow and preventing any potential leaks. Elbows, another key fitting, provide directional changes in the piping, typically available in 45-degree and 90-degree angles. This versatility is vital for navigating around obstacles and optimizing the layout of a system without impeding performance.
In addition to couplings and elbows, tees and reducers play a significant role in various piping applications. Tees allow for branching off from the main pipeline, enabling connections to additional pipes for distributing flow effectively. Reducers, on the other hand, are instrumental in transitioning between different pipe sizes, ensuring that the fluid dynamics remain intact while adapting to varying system requirements. These fittings, alongside others like valves and flanges, form the backbone of an efficient piping system, catering to diverse operational needs and enhancing overall functionality.
In modern piping systems, the role of valves is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring safety. Key valves, such as gate, globe, ball, and check valves, are integral to effectively controlling flow and pressure within the infrastructure. According to a report from the Global Market Insights, the valve market is projected to surpass $100 billion by 2027, driven by increasing demand across industries like oil and gas, water treatment, and power generation. These valves not only regulate the flow of liquids and gases but also prevent backflow, which can lead to significant system failures and safety hazards.
The selection of appropriate valves can significantly influence the performance of piping systems. For instance, globe valves are often preferred for applications where flow regulation is paramount due to their design that allows for smooth throttle control. On the other hand, ball valves provide excellent sealing capabilities and quick shut-off, making them ideal for high-pressure situations. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology indicates that proper valve selection can reduce energy costs by up to 20%, highlighting the economic benefits of investing in high-quality, efficient valve technologies. The right combination of valves can ensure optimal performance, longevity of the piping systems, and compliance with safety regulations.
Elbows and bends are essential components in piping systems, playing a pivotal role in redirecting fluid flow with minimal resistance. By altering the direction of the pipeline, these fittings help maintain the system's efficiency and integrity. When designed properly, elbows and bends can significantly reduce turbulence and pressure loss, which are critical factors in the overall performance of fluid transport systems. Their geometry allows for smooth transitions that enable fluid to change direction seamlessly, minimizing the potential for cavitation and ensuring a steady flow.
Incorporating elbows and bends into a piping system must be done with careful consideration of the fluid dynamics involved. The angles at which these fittings are placed, whether they be 45 or 90 degrees, can drastically affect flow characteristics. For instance, a 45-degree elbow generally offers less resistance compared to a 90-degree elbow, making it a more efficient choice for applications that prioritize flow rate. Additionally, maintaining the proper radius for bends—particularly in larger pipes—can facilitate an unhindered transition, further optimizing the system's performance. Thus, selecting the right elbows and bends is crucial for achieving a piping system that operates efficiently and effectively.
In the realm of pipeline design, tees and crosses play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient transport of fluids across various systems. Tees are primarily used to create branch connections within a pipeline, allowing for fluid to flow in multiple directions. This functionality is essential in distributing resources effectively and can significantly enhance the overall efficiency of a piping system. The design of tees ensures that minimal turbulence occurs during fluid transition, which helps in maintaining the pressure and flow rates required for operational excellence.
Cross fittings, on the other hand, provide an even more complex intersection point within a piping system. By allowing four pipes to intersect, crosses are particularly beneficial in scenarios where multiple lines converge. This capability is invaluable in large-scale industrial setups, where the convergence of different fluid streams is frequent. The efficient design of crosses helps reduce the potential for blockages and allows for better maintenance access across various pipelines. Together, tees and crosses are fundamental to creating a robust and efficient piping infrastructure, ensuring that fluid dynamics are optimized for peak performance.
When it comes to ensuring the durability and efficiency of piping systems, the selection and installation of fittings and valves are crucial. According to the Fluid Power Journal, improper installation can lead to pressure drops of up to 25%, which not only compromises system performance but also leads to premature equipment failure. Therefore, understanding the best practices for choosing fittings and valves becomes vital. It is essential to consider the material compatibility with the fluids being transported, as well as the working pressure and temperature ranges. For example, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) fittings are often recommended for their resistance to corrosion, while brass and stainless steel are favored in high-pressure applications due to their strength and durability.
Additionally, proper installation techniques significantly influence the longevity of fittings and valves. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) emphasizes that following detailed installation guidelines and torque specifications can reduce the risk of leaks and mechanical failures. Utilizing proper sealing methods, such as thread sealants and O-rings, is essential for maintaining system integrity. The importance of regular maintenance should also not be overlooked; the International Journal of Mechanical Engineering suggests that a well-maintained system can extend the life of fittings and valves by up to 30%, demonstrating the clear link between best practices in selection and installation and overall system reliability.